Local governments are being asked to do more with less. Budgets are tight. Teams are stretched. And citizen expectations continue to grow. Whether it’s a city hall, public clinic, or permit office, the pressure to deliver faster and more reliable service is only rising.
But without clear visibility into needs and capacity, resources often end up spread too thin or poorly timed. That’s where smart allocation comes in.
When done right, it helps reduce waste, improve service quality, and build public trust.
In this blog, we’ll walk through 7 practical strategies to help local governments make better use of their people, time, and tools—so that every resource goes further and works better.
What Is Resource Allocation in Government?
In government, resource allocation means deciding how to use your staff, budget, time, and tools. The goal is to cover essential services without overloading any one area.
It affects everything from:
how many people are on shift at a city office,
to how funds are split between infrastructure and housing,
to which community programs stay open.
Done right, it helps you stay fair and focused. Done poorly, it leads to delays, burnout, and public frustration.
The Allocation Function in Government Operations
This is more than just dividing resources. It’s about making sure they support your broader policy goals. The allocation function connects the dots between planning and action.
It plays a role in:
annual budget decisions,
tracking performance across departments,
improving how services reach citizens.
When aligned with real needs, good allocation helps agencies do more with less. It also builds public trust by showing that every dollar and every minute are being used wisely.
Also read - Queue Management Systems: Cost vs. Benefits Analysis for Public Sector Agencies
7 Key Strategies for Efficient Resource Allocation
Getting the most out of your resources starts with knowing where they’re needed most. These strategies help make better use of what you already have.
1. Use Data to Guide Decisions
Good resource allocation starts with good information. If you’re guessing where the pressure points are, you’ll always be one step behind.
Instead, look at real numbers:
average wait times across departments
daily service volumes and foot traffic
staff capacity versus actual demand
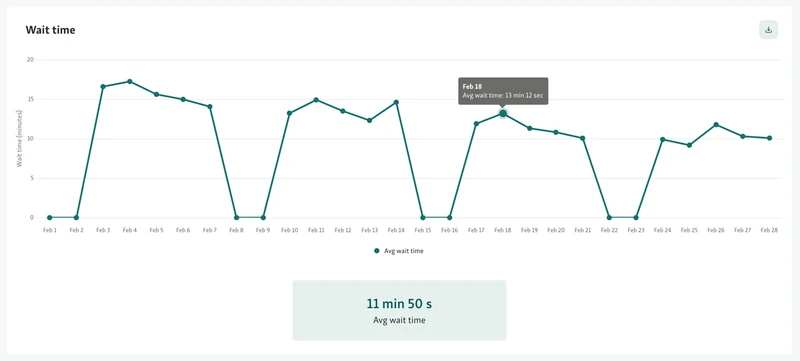
This kind of data shows where time and resources are being used—and where they’re falling short. It’s a critical part of the allocation function in government.
With a tool like Qminder, you can track these patterns in real time. It gives you a clear picture of citizen flow and service use, so you can adjust quickly and allocate smarter. That’s the first step toward getting ahead of the curve.
Read also - The Problem With Government Office Wait Times And How to Solve It
2. Prioritize Based on Urgency and Impact
When everything feels urgent, nothing moves. That’s why setting clear priorities matters.
Some services just can’t wait — like emergency permits, legal filings, or anything tied to safety. Others, while still important, can be spaced out without causing harm.
Break things down into simple tiers:
Essential services that keep operations running or meet legal deadlines
Supportive services that improve access or experience but don’t need an immediate fix
This helps staff know where to focus and gives citizens a fair system to rely on. It’s one of the most practical ways to apply the allocation function in government without overcomplicating the process.
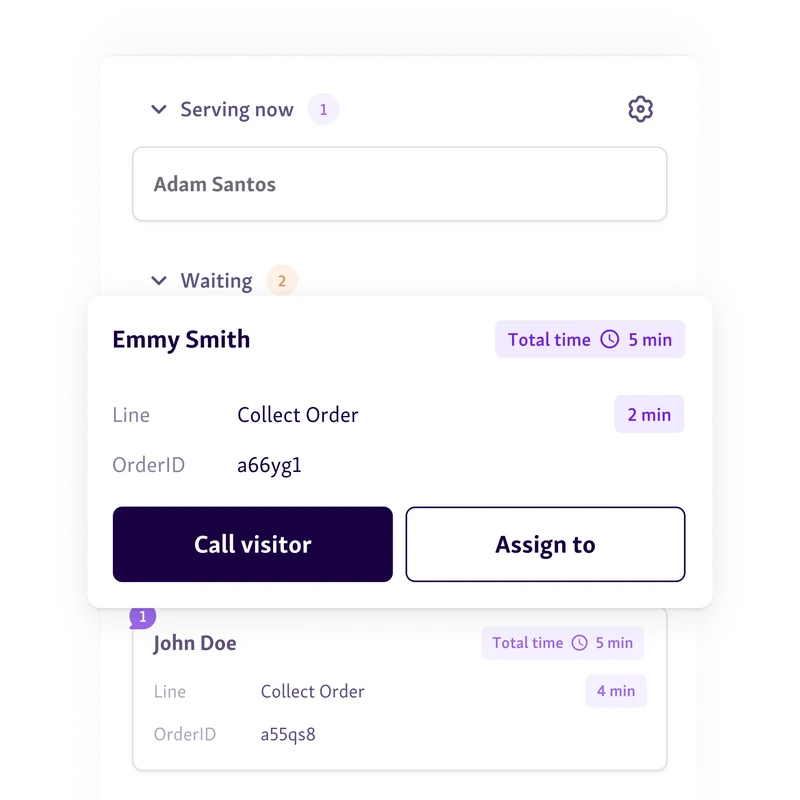
3. Deploy Cross-Department Collaboration
Most local government services don’t work in isolation. But their resources often do. That’s where the gap begins.
If two departments serve the same people, they can also share the same tools and support.
A greeter at the city hall entrance can guide people to the tax office, licensing, or building permits
One check-in system can handle visitors for multiple services under the same roof
A shared service dashboard helps staff coordinate without jumping between systems
It’s not just about saving time. It’s about using every resource to its full potential. And that’s where the allocation function in government really shows its value.
Also read - How Queue Management Software Helps Government Offices
4. Invest in Scalable Technology
When local offices rely too much on manual processes, things break down fast. A short-staffed day or a sudden surge in visitors is all it takes.
That’s why scalable technology matters. Tools like digital queue systems or appointment scheduling software help manage demand without extra strain on staff.
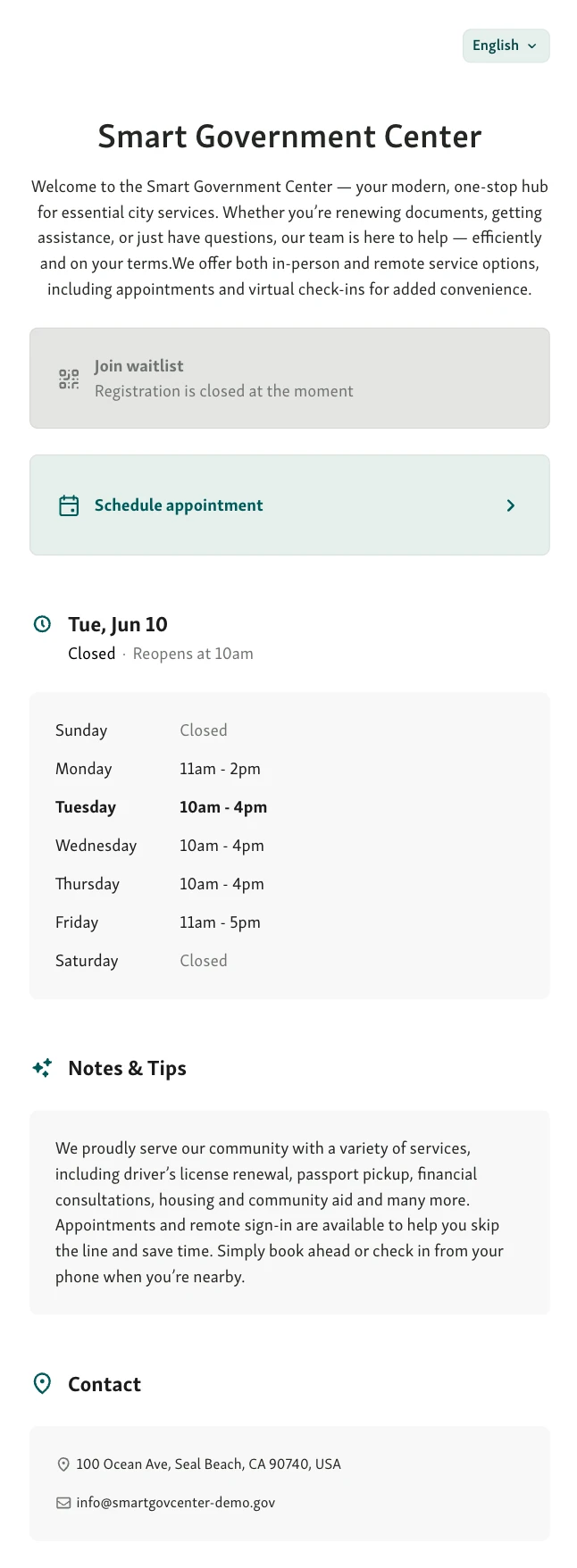
A virtual queuing system lets people check in remotely and wait from anywhere
Staff get real-time visibility into wait times, visitor flow, and service types
Offices can serve more people without adding more lines or paperwork
DMVs across the U.S. are already using virtual queue tools to improve service. It’s one of the easiest ways to stretch limited resources further—without compromising experience.
5. Monitor and Adjust in Real Time
Planning helps, but things don’t always go as expected. Some days, the front desk gets slammed. Other times, lines stack up for one service while another sits empty.
That’s where real-time tracking makes a difference. It gives staff a clear view of what’s happening right now, not just what happened yesterday.
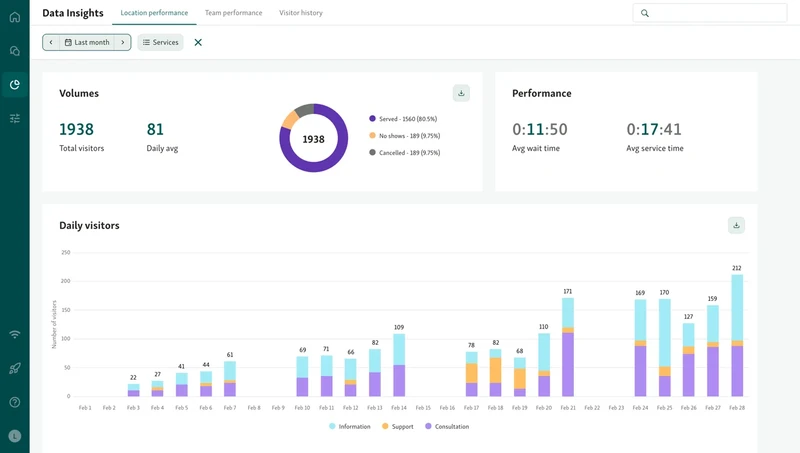
Watch live data on foot traffic and wait times
Move staff around based on what’s building up
Spot slowdowns early and act before things get stuck
Let’s say the building permit counter starts getting crowded. Instead of letting it pile up, a manager can shift support from another section to balance the flow. It’s small changes like this that keep things running smoothly.
6. Build Flexibility into Budgeting and Staffing
Budgets are tight, and needs change fast. If your staffing plan can’t shift with demand, small issues turn into backlogs. That’s why flexibility matters.
Build room in your budget for adjustments. You don’t need to overspend—just plan for the ups and downs.
Keep part-time or on-call staff for busy days
Use hourly data to schedule based on actual demand
Shift resources between departments when needed
For example, if Mondays at the DMV always run long, bring in extra coverage just for those hours. It’s a simple fix that prevents stress—for both your team and the public.
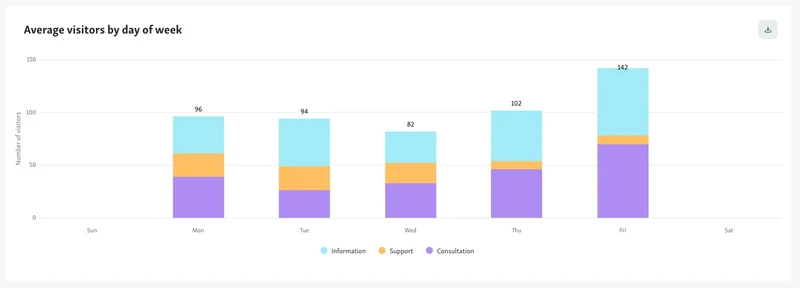
7. Encourage Staff Training and Multi-Skilling
When teams are trained to handle more than one role, it becomes easier to shift resources without slowing things down. A front-desk employee who can also support intake during peak hours adds real value. It gives managers more options and reduces pressure during unexpected absences or spikes in demand.
Cross-train staff to handle basic functions across departments
Rotate roles during slower periods to build confidence
Focus on both technical skills and people-facing tasks
You won’t need to overhire or scramble every time someone’s out sick. With the right training, your team can step in where needed and keep services moving.
You might also like - 7 Insanely Powerful Strategies to Manage Customer Wait Times
Taking Action on Smarter Resource Allocation
Efficient resource allocation in government isn’t just about numbers. It’s about understanding where the needs are, using tools that help you see patterns, and staying flexible as demand shifts.
From cross-department teamwork to scalable technology and real-time data, these strategies help local offices serve better without burning out staff or wasting budget.
Qminder brings many of these ideas together. It helps manage queues, gather data, and streamline the visitor journey across departments.
If you’re ready to modernize your allocation function, book a demo and see how Qminder fits your team.
Resource planning is about anticipating future demands and pre-positioning resources. Resource allocation is the act of deciding in the moment where resources should be assigned.
Yes, they will benefit. The scale may differ but many of the same principles exist, such as leveraging real time data, prioritizing service needs, and flexible staffing approaches regardless of size.
The effectiveness of resource allocation can be fostered by tracking performance indicators (KPIs) such as average service wait times, service coverage rates and staff utilization. These can account for impact and allow for changes in practice.